- Home
-
Products
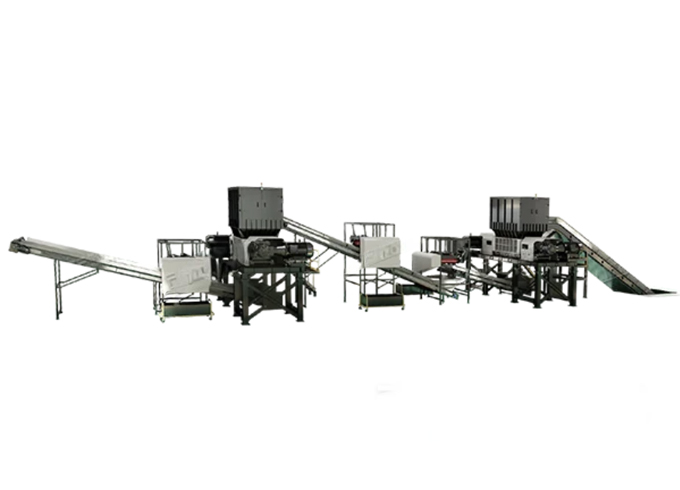
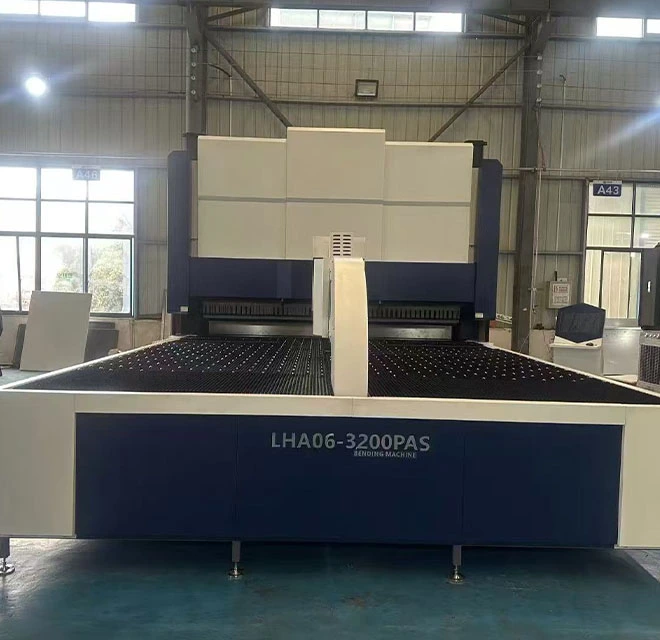
Laser Cutting Machine 3D Cutting Robotic Arm Automatic Loading and Unloading Laser Cutter Single Table Fiber Laser Cutting Machine Dual-use Fiber Laser Cutting MachineHydraulic Press C Frame Hydraulic Press for Sale APA Pneumatic C Frame Power Press for Sale APA Pneumatic Press Machine J21S Deep Throat Punching MachinePlate Rolling Machine W11F Asymmetric 3-Rollers Plate W11 3-Roll Plate Roller Machine W12 4-Rolls Sheet Metal Plate B W11S 3-Rollers Variable GeometryPress Brake Tooling AMADA Press Brake Parts TRUMPF Press Brake Tooling (WILA) Press Brake Tooling for LVD Press Brake Tooling for BYSTRONICShredding Machine LYX Series Mini Shredder Machine LYXS-H Large Planetary Shredder LYXS-P Tire Shredder LY2X Double Shaft ShredderSingle Shaft Shredder LYPS Single Shaft Shredder Machine for Sale Rasper Heavy Duty Single Shaft Shredder
- System & Solutions
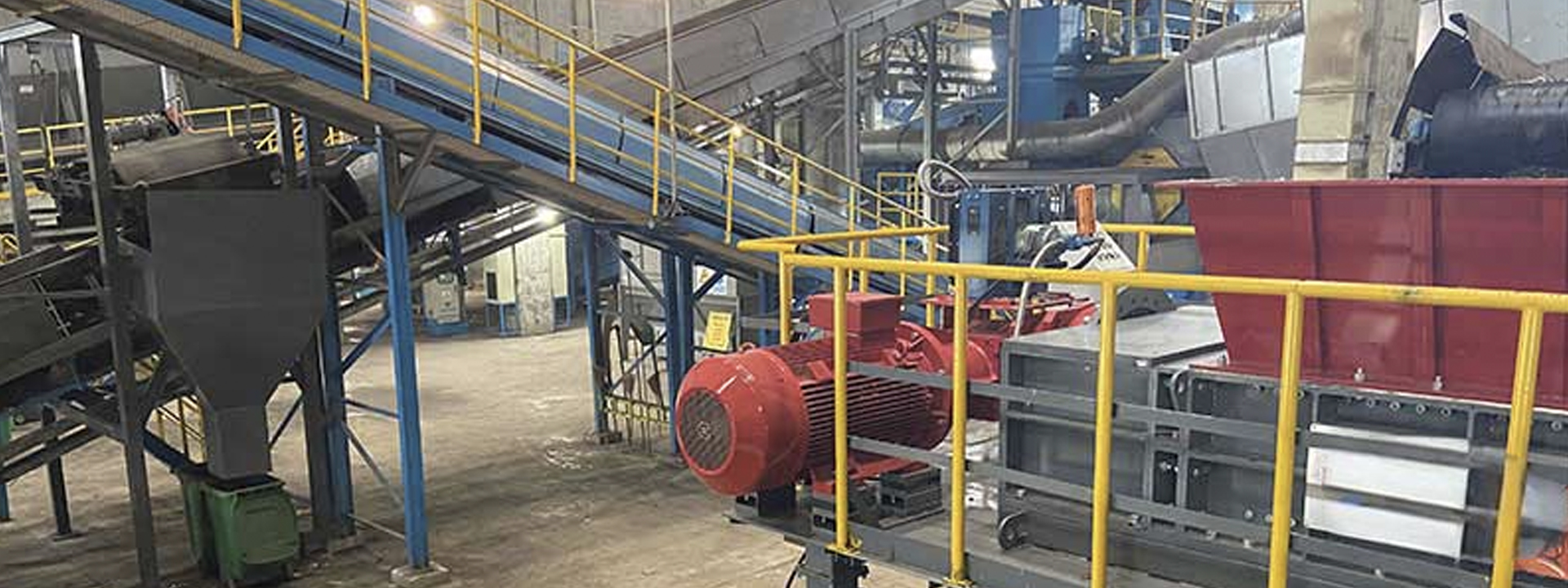
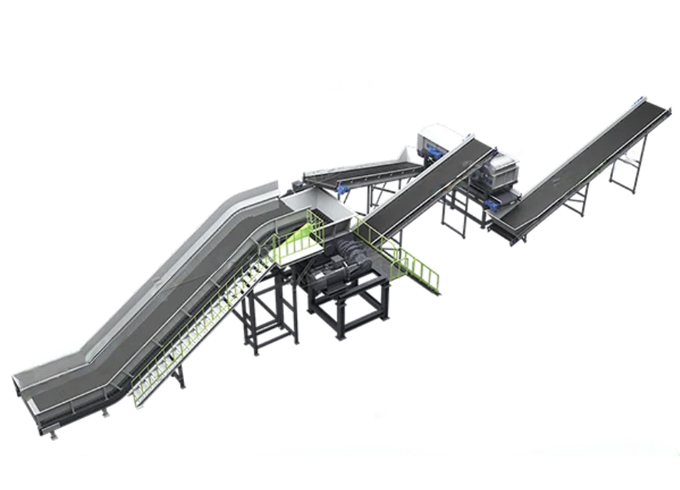
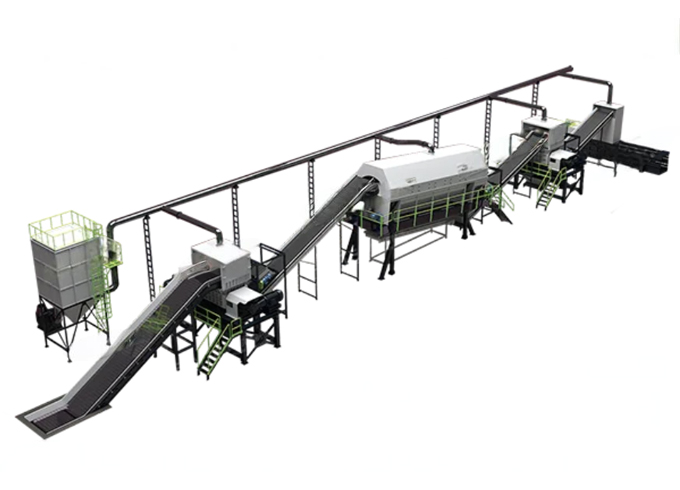
- Recycling Solutions
- Production Process
- Company
- Support
- Contact
 English
English 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 français
français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español русский
русский Türkçe
Türkçe português
português العربية
العربية Polska
Polska हिंदी
हिंदी Indonesia
Indonesia